Nitrogen Trifluoride on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Nitrogen trifluoride () is an
 is a
is a  Since 1992, when less than 100 tons were produced, production has grown to an estimated 4000 tons in 2007 and is projected to increase significantly. World production of NF3 is expected to reach 8000 tons a year by 2010. By far the world's largest producer of is the US
Since 1992, when less than 100 tons were produced, production has grown to an estimated 4000 tons in 2007 and is projected to increase significantly. World production of NF3 is expected to reach 8000 tons a year by 2010. By far the world's largest producer of is the US
NF3
Code of Practice (European Industrial Gas Association)]
WebBook page for NF3
{{DEFAULTSORT:Nitrogen Trifluoride Inorganic amines Nitrogen fluorides Greenhouse gases Industrial gases Nitrogen(III) compounds
inorganic
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as '' inorganic chemist ...
, colorless, non-flammable
A combustible material is something that can burn (i.e., ''combust'') in air. A combustible material is flammable if it ignites easily at ambient temperatures. In other words, a combustible material ignites with some effort and a flammable mat ...
, toxic
Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a subst ...
gas with a slightly musty odor. It finds increasing use within the manufacturing of flat-panel display
A flat-panel display (FPD) is an electronic display used to display visual content such as text or images. It is present in consumer, medical, transportation, and industrial equipment.
Flat-panel displays are thin, lightweight, provide better li ...
s, photovoltaic
Photovoltaics (PV) is the conversion of light into electricity using semiconducting materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect, a phenomenon studied in physics, photochemistry, and electrochemistry. The photovoltaic effect is commercially us ...
s, LED
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor Electronics, device that Light#Light sources, emits light when Electric current, current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy i ...
s and other microelectronics
Microelectronics is a subfield of electronics. As the name suggests, microelectronics relates to the study and manufacture (or microfabrication) of very small electronic designs and components. Usually, but not always, this means micrometre-sc ...
. Nitrogen trifluoride is also an extremely strong and long-lived greenhouse gas
A greenhouse gas (GHG or GhG) is a gas that Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorbs and Emission (electromagnetic radiation), emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse ...
. Its atmospheric burden exceeded 2 parts per trillion
In science and engineering, the parts-per notation is a set of pseudo-units to describe small values of miscellaneous dimensionless quantities, e.g. mole fraction or mass fraction. Since these fractions are quantity-per-quantity measures, they ...
during 2019 and has doubled every five years since the late 20th century.
Synthesis and reactivity
Nitrogen trifluoride did not exist in significant quantities on Earth prior to its synthesis by humans. It is a rare example of a binary fluoride that can be prepared directly from the elements only at very uncommon conditions, such as an electric discharge. After first attempting the synthesis in 1903,Otto Ruff
Otto Ruff (12 December 1871 – 17 September 1939) was a German chemist.
Life
Otto Ruff was born in Schwäbisch Hall, Württemberg. After becoming a pharmacist under the supervision of Carl Magnus von Hell (known from the Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky ...
prepared nitrogen trifluoride by the electrolysis of a molten mixture of ammonium fluoride
Ammonium fluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula NH4F. It crystallizes as small colourless prisms, having a sharp saline taste, and is highly soluble in water. Like all fluoride salts, it is moderately toxic in both acute and chronic o ...
and hydrogen fluoride
Hydrogen fluoride (fluorane) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . This colorless gas or liquid is the principal industrial source of fluorine, often as an aqueous solution called hydrofluoric acid. It is an important feedstock i ...
. It proved to be far less reactive than the other nitrogen trihalides nitrogen trichloride
Nitrogen trichloride, also known as trichloramine, is the chemical compound with the formula NCl3. This yellow, oily, pungent-smelling and explosive liquid is most commonly encountered as a byproduct of chemical reactions between ammonia-derivative ...
, nitrogen tribromide
Nitrogen tribromide is a chemical compound with the formula NBr3. It is extremely explosive in its pure form, even at −100 °C, and was not isolated until 1975. It is a deep-red and volatile solid.
Preparation
NBr3 was first prepared by r ...
and nitrogen triiodide
Nitrogen triiodide is an inorganic compound with the formula N I3. It is an extremely sensitive contact explosive: small quantities explode with a loud, sharp snap when touched even lightly, releasing a purple cloud of iodine vapor; it can even b ...
, all of which are explosive. Alone among the nitrogen trihalides it has a negative enthalpy of formation. It is prepared in modern times both by direct reaction of ammonia and fluorine and by a variation of Ruff's method.Philip B. Henderson, Andrew J. Woytek "Fluorine Compounds, Inorganic, Nitrogen" in Kirk‑Othmer ''Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology'', 1994, John Wiley & Sons, NY. Article Online Posting Date: December 4, 2000 It is supplied in pressurized cylinders.
is slightly soluble in water without undergoing chemical reaction. It is nonbasic with a low dipole moment of 0.2340 D. By contrast, ammonia is basic and highly polar (1.47 D). This difference arises from the fluorine atoms acting as electron withdrawing groups, attracting essentially all of the lone pair electrons on the nitrogen atom. NF3 is a potent yet sluggish oxidizer.
It oxidizes hydrogen chloride to chlorine:
:2 NF3 + 6 HCl → 6 HF + N2 + 3 Cl2
It is compatible with steel and Monel
Monel is a group of alloys of nickel (from 52 to 67%) and copper, with small amounts of iron, manganese, carbon, and silicon. Monel is not a cupronickel alloy because it has less than 60% copper.
Stronger than pure nickel, Monel alloys are res ...
, as well as several plastics.
It converts to tetrafluorohydrazine
Tetrafluorohydrazine or perfluorohydrazine, , is a colourless, reactive inorganic gas. It is a fluorinated analog of hydrazine. It is a highly hazardous chemical that explodes in the presence of organic materials.
Tetrafluorohydrazine is manufac ...
upon contact with metals, but only at high temperatures:
:2 NF3 + Cu → N2F4 + CuF2
NF3 reacts with fluorine and antimony pentafluoride
Antimony pentafluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula Sb F5. This colourless, viscous liquid is a valuable Lewis acid and a component of the superacid fluoroantimonic acid, formed when mixing liquid HF with liquid SbF5 in a 2:1 ratio. ...
to give the tetrafluoroammonium
The tetrafluoroammonium cation (also known as perfluoroammonium) is a positively charged polyatomic ion with chemical formula . It is equivalent to the ammonium ion where the hydrogen atoms surrounding the central nitrogen atom have been replaced ...
salt:
: NF3 + F2 + SbF5 → NFSbF
Mixtures of NF3 and B2H6 are explosive even at cryogenic temperatures, reacting to produce nitrogen gas
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at seventh ...
, boron trifluoride
Boron trifluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula BF3. This pungent, colourless, and toxic gas forms white fumes in moist air. It is a useful Lewis acid and a versatile building block for other boron compounds.
Structure and bondin ...
, and hydrofluoric acid
Hydrofluoric acid is a Solution (chemistry), solution of hydrogen fluoride (HF) in water. Solutions of HF are colourless, acidic and highly Corrosive substance, corrosive. It is used to make most fluorine-containing compounds; examples include th ...
.
Applications
Etching
Nitrogen trifluoride is primarily used to removesilicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic tab ...
and silicon-compounds during the manufacturing of semiconductor devices such as LCD displays, some thin-film solar cell
A thin-film solar cell is a second generation solar cell that is made by depositing one or more thin layers, or thin film (TF) of photovoltaic material on a substrate, such as glass, plastic or metal. Thin-film solar cells are commercially use ...
s, and other microelectronics. In these applications is initially broken down within a plasma
Plasma or plasm may refer to:
Science
* Plasma (physics), one of the four fundamental states of matter
* Plasma (mineral), a green translucent silica mineral
* Quark–gluon plasma, a state of matter in quantum chromodynamics
Biology
* Blood pla ...
. The resulting fluorine radicals are the active agents that attack polysilicon
Polycrystalline silicon, or multicrystalline silicon, also called polysilicon, poly-Si, or mc-Si, is a high purity, polycrystalline form of silicon, used as a raw material by the solar photovoltaic and electronics industry.
Polysilicon is produce ...
, silicon nitride
Silicon nitride is a chemical compound of the elements silicon and nitrogen. is the most thermodynamically stable and commercially important of the silicon nitrides, and the term "silicon nitride" commonly refers to this specific composition. It ...
and silicon oxide Silicon oxide may refer to either of the following:
*Silicon dioxide or quartz, SiO2, very well characterized
*Silicon monoxide
Silicon monoxide is the chemical compound with the formula SiO where silicon is present in the oxidation state +2. In ...
. They can be used as well to remove tungsten silicide
Tungsten silicide (WSi2) is an inorganic compound, a silicide of tungsten. It is an electrically conductive ceramic material.
Chemistry
Tungsten silicide can react violently with substances such as strong acids, fluorine
Fluorine is a chemical ...
, tungsten
Tungsten, or wolfram, is a chemical element with the symbol W and atomic number 74. Tungsten is a rare metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively as compounds with other elements. It was identified as a new element in 1781 and first isolat ...
, and certain other metals. In addition to serving as an etchant in device fabrication, is also widely used to clean PECVD
Plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) is a chemical vapor deposition process used to deposit thin films from a gas state (vapor) to a solid state on a substrate. Chemical reactions are involved in the process, which occur after creati ...
chambers.
dissociates more readily within a low-pressure discharge
Low-pressure discharges exist within Gas-discharge lamps. The electric discharges in gases are made under gas pressures from a few millitorr to a little less than atmospheric.
Description
They are most often used in industry to generate plasma. ...
in comparison to perfluorinated compound
A perfluorinated compound (PFC) or perfluoro compound is an organofluorine compound containing only carbon-fluorines and C−C bonds, as well as potentially heteroatoms. Perfluorinated compounds have properties that result from the presence of flu ...
s (PFCs) and sulfur hexafluoride
Sulfur hexafluoride or sulphur hexafluoride (British spelling) is an inorganic compound with the formula SF6. It is a colorless, odorless, non- flammable, and non-toxic gas. has an octahedral geometry, consisting of six fluorine atoms attached ...
(). The greater abundance of negatively-charged free radicals thus generated can yield higher silicon removal rates, and provide other process benefits such as less residual contamination and a lower net charge stress on the device being fabricated. As a somewhat more thoroughly consumed etching and cleaning agent, NF3 has also been promoted as an environmentally preferable substitute for or PFCs such as hexafluoroethane.
The utilization efficiency of the chemicals applied in plasma processes varies widely between equipment and applications. A sizeable fraction of the reactants are wasted into the exhaust stream and can ultimately be emitted into Earth's atmosphere. Modern abatement systems can substantially decrease atmospheric emissions. has not been subject to significant use restrictions. The annual reporting of production, consumption, and waste emissions by large manufacturers has been required in many industrialized countries as a response to the observed atmospheric growth and the international Kyoto Protocol
The Kyoto Protocol was an international treaty which extended the 1992 United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) that commits state parties to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, based on the scientific consensus that (part ...
.
Highly toxic fluorine gas (F2, diatomic fluorine
Fluorine is a chemical element with the symbol F and atomic number 9. It is the lightest halogen and exists at standard conditions as a highly toxic, pale yellow diatomic gas. As the most electronegative reactive element, it is extremely reacti ...
) is a climate neutral
Carbon neutrality is a state of net-zero carbon dioxide emissions. This can be achieved by balancing emissions of carbon dioxide with its removal (often through carbon offsetting) or by eliminating emissions from society (the transition to the "p ...
replacement for nitrogen trifluoride in some manufacturing applications. It requires more stringent handling and safety precautions, especially to protect manufacturing personnel.
Nitrogen trifluoride is also used in hydrogen fluoride and deuterium fluoride lasers, which are types of chemical laser
A chemical laser is a laser that obtains its energy from a chemical reaction. Chemical lasers can reach continuous wave output with power reaching to megawatt levels. They are used in industry for cutting and drilling.
Common examples of chemical ...
s. There it is also preferred to fluorine gas due to its more convenient handling properties
Greenhouse gas
 is a
is a greenhouse gas
A greenhouse gas (GHG or GhG) is a gas that Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorbs and Emission (electromagnetic radiation), emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse ...
, with a global warming potential
Global warming potential (GWP) is the heat absorbed by any greenhouse gas in the atmosphere, as a multiple of the heat that would be absorbed by the same mass of carbon dioxide (). GWP is 1 for . For other gases it depends on the gas and the time f ...
(GWP) 17,200 times greater than that of when compared over a 100-year period.
Its GWP place it second only to in the group of Kyoto-recognised greenhouse gases, and was included in that grouping with effect from 2013 and the commencement of the second commitment period of the Kyoto Protocol. It has an estimated atmospheric lifetime
A greenhouse gas (GHG or GhG) is a gas that Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorbs and Emission (electromagnetic radiation), emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse ...
of 740 years, although other work suggests a slightly shorter lifetime of 550 years (and a corresponding GWP of 16,800).
Although has a high GWP, for a long time its radiative forcing
Radiative forcing (or climate forcing) is the change in energy flux in the atmosphere caused by natural or anthropogenic factors of climate change as measured by watts / metre2. It is a scientific concept used to quantify and compare the external ...
in the Earth's atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing for ...
has been assumed to be small, spuriously presuming that only small quantities are released into the atmosphere. Industrial applications of routinely break it down, while in the past previously used regulated compounds such as and PFCs were often released. Research has questioned the previous assumptions. High-volume applications such as DRAM
Dynamic random-access memory (dynamic RAM or DRAM) is a type of random-access semiconductor memory that stores each bit of data in a memory cell, usually consisting of a tiny capacitor and a transistor, both typically based on metal-oxid ...
computer memory production, the manufacturing of flat panel displays
A flat-panel display (FPD) is an electronic display device, display used to display visual content such as text or images. It is present in consumer, medical, transportation, and industrial equipment.
Flat-panel displays are thin, lightweight, p ...
and the large-scale production of thin-film solar cell
A thin-film solar cell is a second generation solar cell that is made by depositing one or more thin layers, or thin film (TF) of photovoltaic material on a substrate, such as glass, plastic or metal. Thin-film solar cells are commercially use ...
s use .
 Since 1992, when less than 100 tons were produced, production has grown to an estimated 4000 tons in 2007 and is projected to increase significantly. World production of NF3 is expected to reach 8000 tons a year by 2010. By far the world's largest producer of is the US
Since 1992, when less than 100 tons were produced, production has grown to an estimated 4000 tons in 2007 and is projected to increase significantly. World production of NF3 is expected to reach 8000 tons a year by 2010. By far the world's largest producer of is the US industrial gas
Industrial gases are the gaseous materials that are manufactured for use in industry. The principal gases provided are nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, argon, hydrogen, helium and acetylene, although many other gases and mixtures are also avail ...
and chemical company Air Products & Chemicals
Air Products and Chemicals, Inc. is an American international corporation whose principal business is selling gases and chemicals for industrial uses. Air Products' headquarters is in Allentown, Pennsylvania, in the Lehigh Valley region of Pen ...
. An estimated 2% of produced is released into the atmosphere. Robson projected that the maximum atmospheric concentration is less than 0.16 parts per trillion (ppt) by volume, which will provide less than 0.001 Wm−2 of IR forcing.
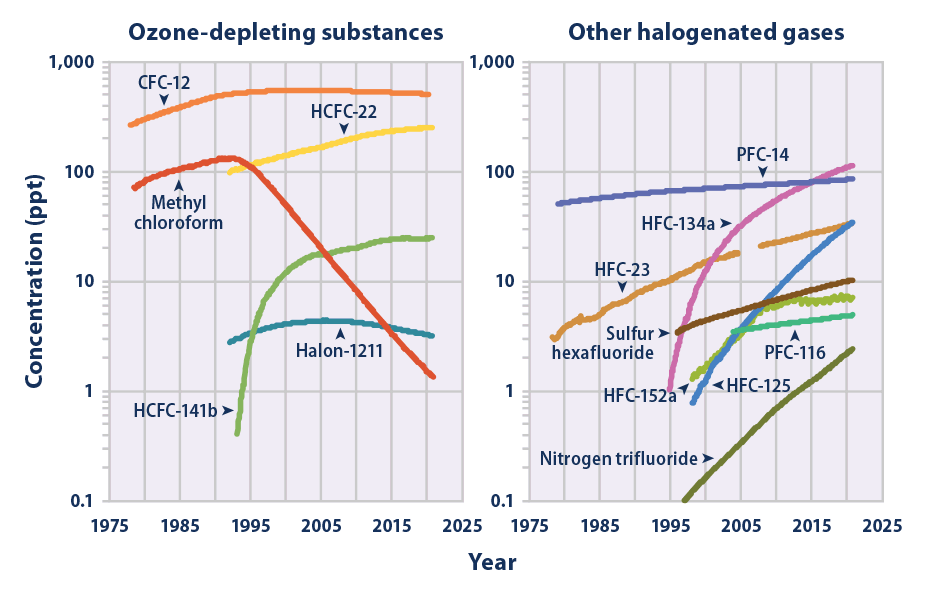
The mean global tropospheric concentration of NF3 has risen from about 0.02 ppt (parts per trillion, dry air mole fraction) in 1980, to 0.86 ppt in 2011, with a rate of increase of 0.095 ppt yr−1, or about 11% per year, and an interhemispheric gradient that is consistent with emissions occurring overwhelmingly in the Northern Hemisphere, as expected. This rise rate in 2011 corresponds to about 1200 metric tons/y NF3 emissions globally, or about 10% of the NF3 global production estimates. This is a significantly higher percentage than has been estimated by industry, and thus strengthens the case for inventorying NF3 production and for regulating its emissions.
One study co-authored by industry representatives suggests that the contribution of the NF3 emissions to the overall greenhouse gas
A greenhouse gas (GHG or GhG) is a gas that Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorbs and Emission (electromagnetic radiation), emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse ...
budget of thin-film Si-solar cell manufacturing is clear.
The UNFCCC
The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) established an international environmental treaty to combat "dangerous human interference with the climate system", in part by stabilizing greenhouse gas concentrations in the ...
, within the context of the Kyoto Protocol, decided to include nitrogen trifluoride in the second Kyoto Protocol
The Kyoto Protocol was an international treaty which extended the 1992 United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) that commits state parties to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, based on the scientific consensus that (part ...
compliance period, which begins in 2012 and ends in either 2017 or 2020. Following suit, the WBCSD/WRI GHG Protocol is amending all of its standards (corporate, product and Scope 3) to also cover NF3.
Safety
Skin contact with is not hazardous, and it is a relatively minor irritant tomucous membrane
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is ...
s and eyes. It is a pulmonary irritant with a toxicity
Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a subst ...
considerably lower than nitrogen oxides Nitrogen oxide may refer to a binary compound of oxygen and nitrogen, or a mixture of such compounds:
Charge-neutral
*Nitric oxide (NO), nitrogen(II) oxide, or nitrogen monoxide
*Nitrogen dioxide (), nitrogen(IV) oxide
*Nitrogen trioxide (), or ni ...
, and overexposure via inhalation causes the conversion of hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin BrE) (from the Greek word αἷμα, ''haîma'' 'blood' + Latin ''globus'' 'ball, sphere' + ''-in'') (), abbreviated Hb or Hgb, is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein present in red blood cells (erythrocyte ...
in blood to methemoglobin
Methemoglobin (British: methaemoglobin) (pronounced "met-hemoglobin") is a hemoglobin ''in the form of metalloprotein'', in which the iron in the heme group is in the Fe3+ (ferric) state, not the Fe2+ (ferrous) of normal hemoglobin. Sometimes, it i ...
, which can lead to the condition methemoglobinemia
Methemoglobinemia, or methaemoglobinaemia, is a condition of elevated methemoglobin in the blood. Symptoms may include headache, dizziness, shortness of breath, nausea, poor muscle coordination, and blue-colored skin (cyanosis). Complications m ...
. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH, ) is the United States federal agency responsible for conducting research and making recommendations for the prevention of work-related injury and illness. NIOSH is part of the C ...
(NIOSH) specifies that the concentration that is immediately dangerous to life or health (IDLH value) is 1,000 ppm.
See also
*IPCC list of greenhouse gases
This is a list of the most influential long-lived, well-mixed greenhouse gases, along with their tropospheric concentrations and direct radiative forcings, as identified by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Abundances of thes ...
*Nitrogen pentafluoride
Nitrogen pentafluoride (NF5) is a theoretical compound of nitrogen and fluorine that is hypothesized to exist based on the existence of the pentafluorides of the atoms below nitrogen in the periodic table, such as phosphorus pentafluoride. Theoret ...
*Tetrafluorohydrazine
Tetrafluorohydrazine or perfluorohydrazine, , is a colourless, reactive inorganic gas. It is a fluorinated analog of hydrazine. It is a highly hazardous chemical that explodes in the presence of organic materials.
Tetrafluorohydrazine is manufac ...
Notes
References
External links
*NF3
Code of Practice (European Industrial Gas Association)]
WebBook page for NF3
{{DEFAULTSORT:Nitrogen Trifluoride Inorganic amines Nitrogen fluorides Greenhouse gases Industrial gases Nitrogen(III) compounds